The right hosting strategy must be chosen because even a one-second delay in page response time can lose you up to 7% of your consumer base. If you want top-notch performance and uptime, Dedicated servers and Cloud servers are two popular options, but these hosting methods are best for various use cases. Which one is the best choice for your company’s requirements? Let’s discuss the Difference Between Dedicated Server and Cloud Server? and choose the best.
This article compares and contrasts cloud and dedicated servers and lists their respective advantages and disadvantages. We give you all the information you require to decide wisely and choose the hosting package that best suits your use case, business requirements, and financial constraints.
What is Cloud Hosting Server?
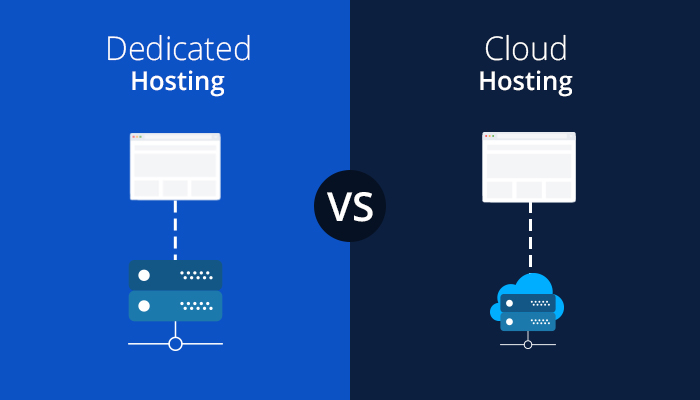
Instead of using a single server, cloud hosting distributes data over a number of devices. Users can access the various cloud servers by utilizing a “virtual computer” to handle their data. The fact that cloud hosting utilizes the processing power and services of several computers differentiates it from dedicated server hosting.
Many of the new retail dedicated cloud hosting plans for small business website publishing support is built on webserver network management software advancements derived from “big data” in enterprise corporations.
DevOps teams in IT firms like Google, Facebook, Microsoft, Oracle, and IBM, as well as other hosting companies like Arzhost web hosting company, Rackspace, and Amazon., are responsible for meeting the scalability requirements of the largest websites in the world.
How Do Cloud Hosts Operate?
It is first vital to comprehend how cloud servers function before comparing them to dedicated servers. Cloud hosting makes use of a virtual server that disperses data among connected computers situated in various locations using cloud computing technology.
Understanding how public, private, hybrid, and managed cloud hosting frameworks relate to the unique web hosting needs of small businesses, SMEs, start-up software companies, and enterprise corporations (such as multinationals or Fortune 500 brands) is crucial. Each market sector has different cost-saving solutions, so it’s important to understand how these services relate to each of these market sectors.
The distinctions between Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) plans are also important for business website owners to comprehend.
A cloud hosting service’s key benefit is that it enables small businesses to access an enterprise-grade SaaS/PaaS solution for a fraction of the price of developing the software from scratch.
Along with elastic scalability, controlled platform security is what sets cloud hosting plans apart from dedicated server options that have segregated hardware and specialized webserver software stack settings.
Many cloud VPS plans to employ a “pay as you go” payment model as opposed to set rates, enabling them to scale to add additional CPU cores, RAM, or I/O operations as needed to handle sudden increases in web traffic that could otherwise overwhelm shared hosting plans.
Multiple virtual servers and databases are managed by elastic cloud platforms at once, updates are synchronized between versions, and web pages are cached for anonymous browsers.
Whether you’re using WordPress, Drupal, or Joomla and programming in PHP,.NET, Linux, Windows, or another language, cloud hosting enables you to easily launch and maintain your sites.
Principal Difference Between Dedicated Server and Cloud Server?
An important step in the process of a firm creating its online presence is comparing the Difference Between Dedicated Server and Cloud Server. The choice ultimately depends on how each server meets the demands of a specific organization.
Cloud hosting solutions offer web server resource scalability alternatives that compete at the same price levels as dedicated server hardware for heavy-traffic websites for the majority of small business web hosting requirements.
Dedicated server plans are essential because many cloud platforms utilize a single web server stack software that cannot support the specialized software requirements of older web applications or databases.
For better webserver performance at scale with the integrated page caching, small business owners can typically convert their existing websites to cloud hosting plans that offer a “plug and play” PaaS option.
Dedicated servers offer the underlying hardware resources that programmers can specifically equip with the third-party frameworks, tools, and programming language extensions needed to create sophisticated, database-driven online and mobile apps.
Based on virtualization and thousands of active domain names on a single server instance, which is possible with shared hosting vs. dedicated hosting, over-provisioning dedicated server hardware for web and mobile applications can result in superior performance.
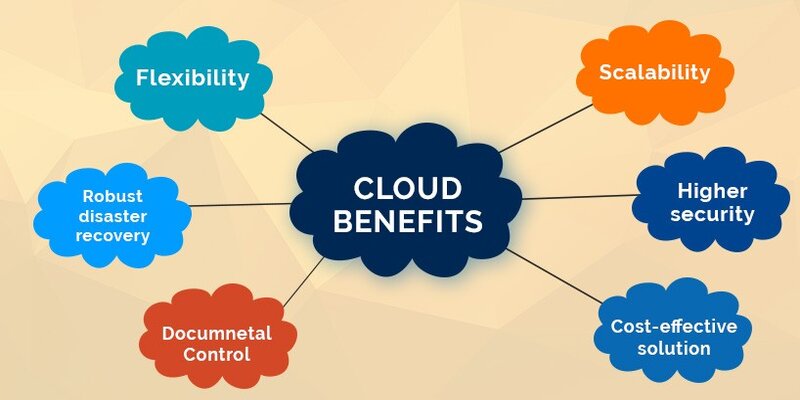
Benefits of Cloud Hosting
The main benefit of cloud hosting plans is that they come with pre-installed elastic web server support and custom stack software that is tailored for CMS websites running on LAMP. Despite the fact that there are many different clouds hosting plans, platforms, and services available, each unique to the business and programming team developing them for the market.
Through a mix of high-end hardware configurations, SSD storage solutions, load balancing on network traffic, multi-layered database, PHP process, and web file caching services, including CDN integration, CMS site owners benefit from higher overall performance on cloud hosting.
In comparison to shared hosting plans, cloud hosting gives CMS websites additional RAM, CPU cores, and I/O processes while enabling each site to grow to use more resources as needed in accordance with the demands of actual production web traffic. This guarantees that websites are “always on” regardless of online traffic conditions and that web pages load more quickly under typical community usage.
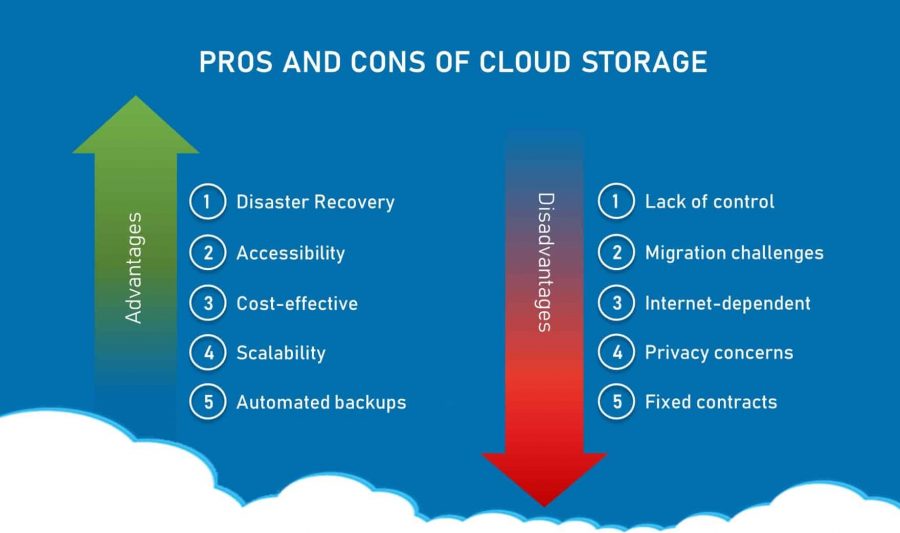
Hosting in the Cloud Has Drawbacks
The lack of full flexibility for systems administrators or web developers to modify the web server stack software installation in order to create unique solutions is one of the drawbacks of retail cloud hosting under the PaaS model compared to a dedicated server plan.
On retail PaaS cloud hosting services, for instance, there is no provision for changing the operating system or setting up different web server platforms like Nginx, Tomcat, Hadoop, Lightspeed, or Lighted.
However, “pay as you go” cloud hosting solutions offered by AWS, Google Cloud, and other businesses do make it simple to customize the webserver stack. When switching from shared hosting to cloud computing for better performance, small business owners typically find managed WordPress hosting and retail cloud plans offered with LAMP PaaS options easier to use.
Difference Between Dedicated Server and Cloud Server? However, the cloud computing plans offered with more stack flexibility require experience in systems administration and work similarly to VPS plans.
How Does Hosting for Dedicated Servers Operate?
Without examining the operation of dedicated servers, the Difference Between a Dedicated Server and a Cloud Server? cannot be made. Businesses can rent dedicated servers from hosting companies, and they can then have the server configured and customized to meet their unique requirements.
Dedicated servers have historically been advantageous because system administrators may set them up for the precise amount of web traffic needed to sustain online operations.
Where this varies, website owners must set up dedicated servers with excess capacity so they can run better when traffic volume is lower than the peak.
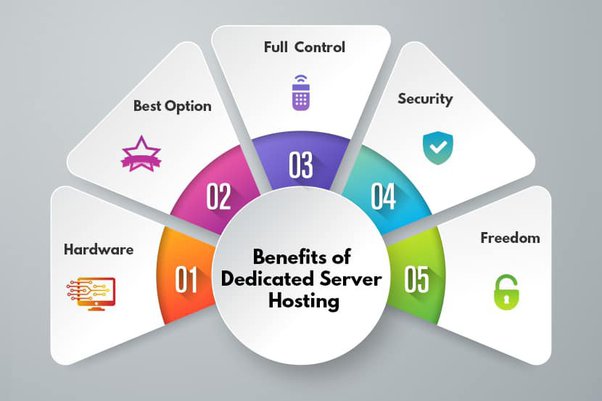
Benefits of Dedicated Server Hosting
A significant benefit of dedicated servers is customization. Companies who need to manage high volumes of traffic or operate complex applications frequently discover that the cost differences between cloud and dedicated servers are less significant than having a service tailored to their specific requirements.
Dedicated server hardware is needed by web developers and programmers to build unique web server environments for complicated application support.
This can involve installing different web server operating systems, unique developer extensions for programming languages, performance-improving tools like sophisticated page caching systems, or different MySQL database frameworks.
Developers of Java, ASP.NET, Node.js, PHP, and Python need specialized server hardware that can be fully configured to create new applications or support dated online software with certain runtime needs. High amounts of online traffic for eCommerce, media, publishing, promotions and other uses can be supported by dedicated servers that are optimized for this.
Disadvantages of Dedicated Server Hosting
The biggest drawback of dedicated servers is that they need systems administrators to maintain all facets of online security, including the operating system (OS) and all installed extension frameworks, under an unmanaged method.
Remote technicians in the data center regularly apply security patches to dedicated servers with a managed stack software environment, however, this might lead to data access problems with unregistered personnel that are undesirable for various company processes.
Even while it is challenging to duplicate the speed of fiber optic network resources in a top-tier data center or international colocation facility, the cost of leasing remote dedicated servers might be more expensive than purchasing and configuring the hardware locally.
Trust in the web hosting provider includes relying on a third-party team for operations that can be mission-critical for the support of business websites. But not every hosting provider is guaranteed to be consistent in this at a level that is reliable, potentially resulting in a loss of business or irregular, unpredictable web server downtime.
Selecting the Best Server for Your Company
Difference Between Dedicated Server and Cloud Server? Business owners can now choose cloud hosting plans that grow to deliver more CPU cores, RAM, or database instances automatically as necessary by web traffic (“elastic scaling”), rather than switching from a shared hosting account to a dedicated server with larger hardware resources allocations.
This can be more effective than manually estimating the needed server overcapacity to match peak hours with downtime levels of website traffic when combined with a “pay as you go” strategy or affordable fixed-rate billing.
The ability to build a bespoke webserver software stack platform to support required third-party programming languages and database extensions for complicated online and mobile applications with custom code is the most essential component of web hosting for many company websites.
Dedicated servers have historically been the preferred option, but cloud computing possibilities are emerging as more and more cost-effective substitutes for creating small business software solutions. This heightens the interest in the discussion of dedicated servers vs. cloud servers.
Small businesses and SMEs can now host their websites on retail PaaS cloud hosting plans with elastic server capabilities for a fraction of the price of comparable dedicated hardware and with the same enterprise-quality services that the biggest companies in the world use to maintain their daily internet operations at scale.