Are you looking for the best Types of Firewalls configuration to safeguard your company against threats?
Your decision-making process is aided by your knowledge of firewall operation. This article delineates the various kinds of firewalls so that you can choose one wisely.
How do Types of Firewalls work? A security tool that keeps an eye on network traffic is a firewall. By filtering incoming and outgoing traffic according to a set of predetermined rules, it safeguards the internal network.
The simplest technique to increase security between a system and malicious attacks is to set up a firewall.
What Functions a Types of Firewalls?
A system’s hardware or software may be equipped with a firewall to protect it from harmful traffic. It can safeguard either a single computer or a whole computer network, depending on the configuration. According to pre-established rules, the device examines both incoming and departing traffic.
Data is requested from a sender and sent from a receiver in order to communicate via the Internet. Data is divided into manageable data packets as it cannot be transferred in its whole, making up the initially communicated entity. A firewall’s job is to inspect data packets going to and from the host.
What is inspected by a Types of Firewalls? There is a header (control information) and payload in each data packet (the actual data). The header contains details on the sender and the recipient. The packet must first travel through the firewall before it can use the specified port to enter the internal network.
This transfer is based on the data it contains and how it adheres to the established rules. For instance, the firewall might include a rule that disallows traffic from a particular IP address.
The firewall blocks access if it detects data packets with that IP address in the header. A firewall can similarly restrict access to only the designated trusted sources. This security device can be configured in a variety of ways. Depending on the sort of firewall, it may or may not protect the system at hand.
Various Types of Firewalls
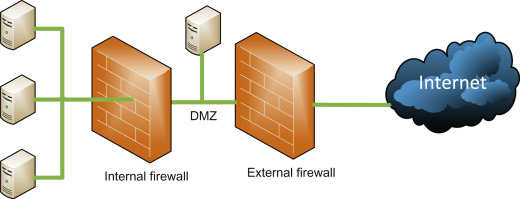
Firewalls can have a wide range of operational strategies and general structures, even though they always work to restrict unwanted access. There are three different kinds of firewalls: hardware firewalls, software firewalls, or both.
The remaining firewall types mentioned on this list are firewall setup options, such as software or hardware.
1: Computer Firewalls
On the host device, a software firewall is deployed. As a result, another name for this kind of firewall is a host firewall. It must use its resources to function because it is attached to a certain object. It will therefore inevitably consume some of the system’s RAM and CPU.
You must install the software on each device if there are several. Each one needs a different configuration because it needs to work with the host. The biggest drawback is therefore the time and expertise required to administer and manage firewalls for each device.
While filtering incoming and outgoing traffic, software firewalls have the advantage of being able to distinguish between different programs. As a result, they are able to grant access to some programs while denying access to others.
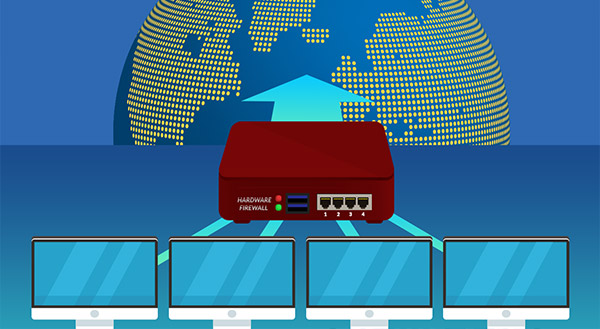
2: Firewalls in hardware
Hardware firewalls, as their name implies, are security tools that act as a barrier between an internal network and an external network (the Internet). This category also goes by the name Appliance Firewall.
A hardware firewall has its own resources and doesn’t need any CPU or RAM from the host devices, in contrast to a software firewall. It is an actual device that acts as a gateway for data traveling to and from an internal network.
They are utilized by medium-sized and large businesses with numerous computers connected to the same network. In such circumstances, using hardware firewalls is more feasible than installing unique software on each device. It takes knowledge and expertise to configure and manage a hardware firewall, therefore ensuring sure a qualified crew is available to do this task.
3: Firewalls with Packet Filtering
The packet-filtering firewall is the most fundamental kind of firewall when it comes to sorts of firewalls depending on how they operate. It functions as a router or switch’s inline security checkpoint. As implied by the name, it keeps an eye on network traffic by sorting incoming packets based on the data they contain.
Each data packet consists of a header and the contents it carries, as was previously stated. Based on the header data, this kind of Types of firewall chooses whether to grant or deny access to a packet. It examines the protocol, source IP address, destination IP address, source port, and destination port to accomplish this. The packets are either passed on or dropped depending on how closely the numbers match the access control list (rules defining wanted/unwanted traffic).
A data packet won’t be permitted to enter the system if it doesn’t adhere to all the necessary rules.
A quick and resource-efficient option is a firewall with packet filtering. It isn’t the safest option, though. The data (payload) itself is not checked; only the header data is examined.
The packet-filtering firewall is not the greatest option for robust system security because malware can also be found in this portion of the data packet.
4: Gateways at the Circuit Level
Circuit-level gateways are a form of firewall that monitors TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) connections and sessions at the session layer of the OSI model. Their main responsibility is to guarantee the security of the established connections.
Circuit-level firewalls are typically incorporated into the software or an existing firewall.
They examine the transactional data rather than the actual data, much like pocket-filtering firewalls. Circuit-level gateways are also useful, easy to set up, and don’t need a separate proxy server.
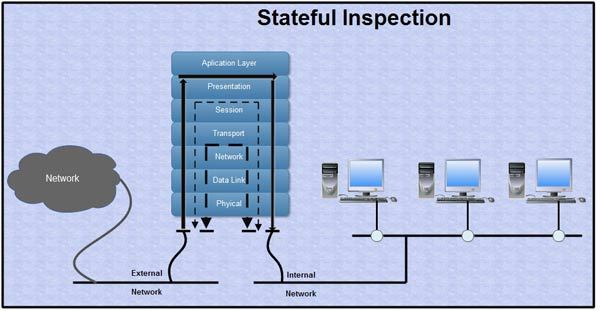
5: Firewalls with Stateful Inspection
By observing the TCP 3-way handshake, a stateful inspection firewall keeps track of the status of a connection. By allowing only expected return traffic to enter, it is able to monitor the entire connection from beginning to end.
The stateful inspection creates a database (state table) and records the connection information when a connection is established and data requests are made.
Each connection’s source IP, source port, destination IP, and destination port are listed in the state table. It dynamically builds firewall rules using the stateful inspection technique to enable expected traffic.
A firewall of this kind is used for added security. In comparison to stateless filters, it imposes more controls and is more secure. Stateful firewalls, in a contrast to stateless/packet filtering, examine the actual data transferred over numerous packets rather than simply the headers. They also demand greater system resources as a result.
6: Firewall Proxy
A proxy firewall acts as a connecting point for internal and external systems using the Internet to communicate. By relaying requests from the original client and disguising them as its own, it secures a network. Proxy, which means to act as a substitute, fulfills that function. It acts as the request’s send the client’s replacement.
The proxy server intercepts the message sent by the client when it requests access to a web page. By impersonating the client, the proxy sends the message to the web server.
By doing this, the client’s identity and location are concealed, shielding it from limitations and potential threats. The proxy then transmits the requested data to the client after receiving a response from the web server.
7: Future-Proof Firewalls
A security tool that combines several features of different firewalls is the next-generation firewall. Packet, stateful, and deep packet inspection are all included. Simply said, NGFW examines the packet’s whole payload rather than just its header data.
The next-generation firewall, in contrast to conventional firewalls, examines every step of the data transaction, including the TCP handshakes and deep and surface-level packet inspection.
Protection from malware attacks, outside threats, and intrusion can be had by using NGFW. These gadgets are extremely adaptable, and the functionalities they provide are not well-defined. Check out the features that each particular option offers as a result.
8: Cloud Firewalls
A cloud-based approach to network protection is a cloud firewall, often known as firewall-as-a-service (Faas). It is managed and operated on the Internet by third-party vendors, just like other cloud solutions.
Cloud firewalls are frequently used by clients as proxy servers, albeit the configuration might change depending on demand. Their primary benefit is scalability. Since they are independent of physical resources. The firewall capacity can be adjusted in accordance with the volume of traffic.
This solution is used by businesses to safeguard their internal networks and other cloud infrastructures (Iaas/Paas).
Which Firewall Architecture Suits Your Business Best?
There is no requirement to be specific when selecting the best Types of Firewalls. Varying types of firewalls can be used for multiple levels of security.
Moreover, keep in mind the following elements:
- The organization’s size: The internal network’s size. Do you require a firewall that keeps an eye on the internal network or can you control a firewall on each device? When choosing between software and hardware firewalls, the answers to these questions are crucial. The IT team selected to oversee the setup will also play a significant role in choosing between the two options.
- The tools at our disposal: Can you afford to put the firewall on a different piece of hardware or even in the cloud, separating it from the internal network? The amount of traffic that the firewall must filter and its consistency are also crucial factors.
- The needed level of security: The variety and quantity of firewalls should correspond to the degree of security needed for the internal network. A company that handles sensitive client information should make sure that data is secure by increasing firewall security.
Create a Type of Firewalls setup that satisfies the standards taking these things into account. Use the ability to layer multiple security measures, and set up the internal network to filter all incoming traffic. See how Arzhost ensures cloud data security for secure cloud options.
Read More: